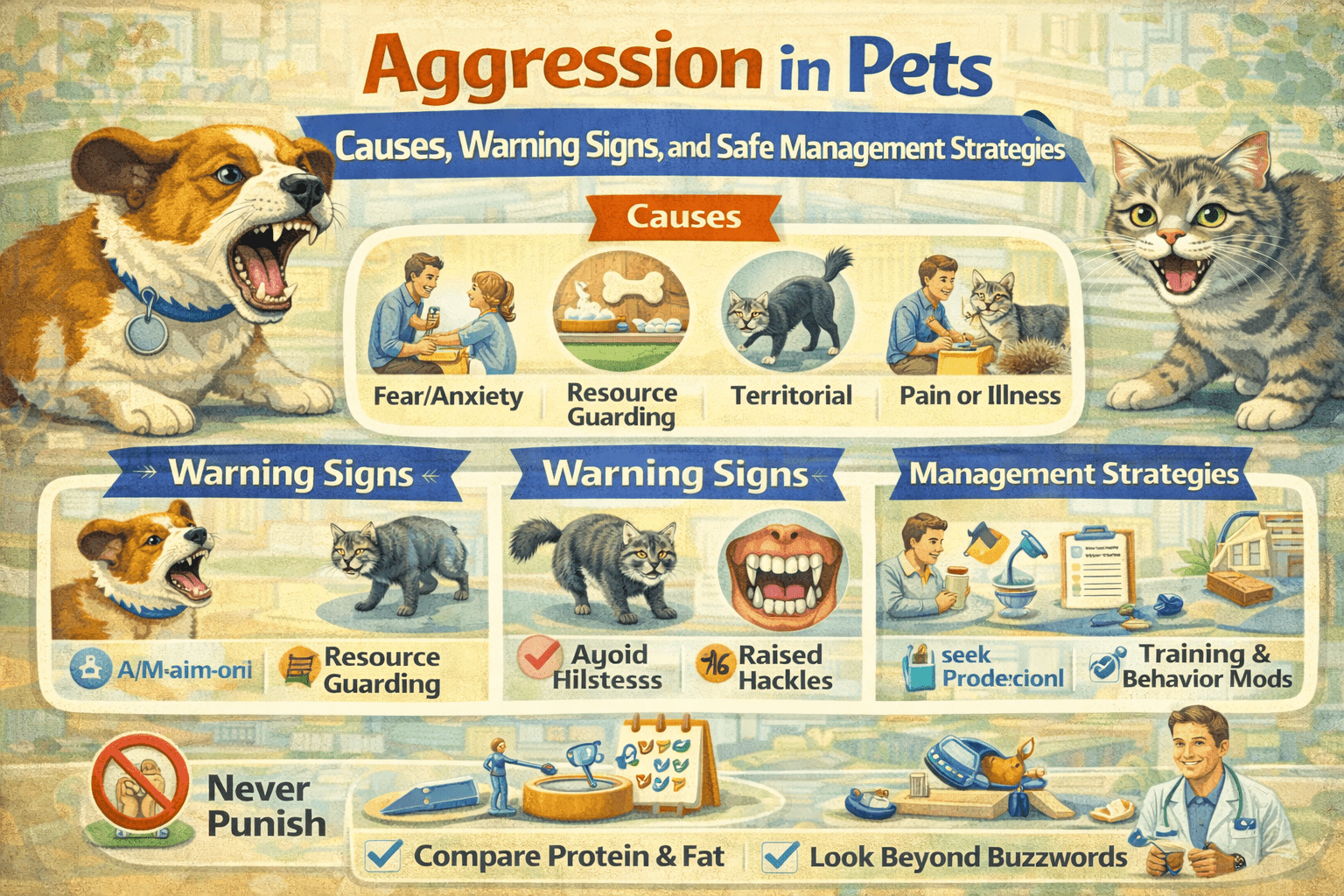
Aggression in Pets: Causes, Warning Signs, and Safe Management Strategies
Introduction
Aggression in pets is one of the most concerning behavior issues owners face. It can be frightening, confusing, and emotionally distressing. Many pets labeled as “aggressive” are actually fearful, stressed, or misunderstood.
This guide explains why aggression happens, how to recognize early warning signs, and how to manage it safely and responsibly—without punishment or fear.
Understanding Aggression as Communication
Aggression is rarely random. It is a response to:
- Fear
- Pain
- Stress
- Resource guarding
- Poor socialization
Punishing aggression suppresses warning signs without solving the cause.
Common Types of Pet Aggression
Fear-Based Aggression
Triggered when a pet feels threatened.
Signs include:
- Growling
- Freezing
- Bared teeth
Resource Guarding
Protecting food, toys, or territory.
This behavior often stems from insecurity, not dominance.
Pain-Induced Aggression
Pets in pain may react defensively.
Sudden aggression always requires medical evaluation.
Territorial Aggression
More common in cats and unneutered pets.
Early Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
- Stiff body posture
- Ears pinned back
- Dilated pupils
- Low growling or hissing
Respect warnings—do not push interaction.
Why Punishment Is Dangerous
Punishment:
- Increases fear
- Removes warning signs
- Raises bite risk
Behavior modification must be force-free.
Safe Management Strategies
Step 1: Identify Triggers
Keep a behavior journal to track:
- Situations
- People or animals involved
- Environment
Patterns reveal causes.
Step 2: Reduce Exposure
Manage the environment to prevent reactions while training progresses.
Step 3: Use Positive Reinforcement
Reward calm behavior in triggering situations.
Step 4: Seek Professional Support
Certified trainers or behaviorists can design safe plans.
Aggression in Cats: Often Misunderstood
Cats may show aggression through:
- Swatting
- Biting
- Hissing
Stress reduction and environmental enrichment are key.
When Aggression Becomes an Emergency
Immediate professional help is required if:
- Bites occur
- Aggression escalates rapidly
- Children or vulnerable people are at risk
🎥 YouTube Video Suggestion:
Conclusion
Aggression is a signal—not a flaw. With patience, understanding, and professional guidance, most aggressive behaviors can be managed safely and humanely.